Comprehending Flow Maintenance Functions
Elaborate Flow Management Perspectives:
Industrial Pipe Cleaning functions as a highly powerful practice primarily useful within the energy and energy gas arenas, yet also revealing comprehensive deployments in the hydric duct frameworks. Fundamentally, it incorporates deploying a apparatus termed a "pig," typically cylindrical in shape, into a pipeline to decontaminate it. These units are multifunctional, handling duties such as taking away deposits including wax, scale, and corrosion, verifying pipeline cohesion, and securing propagation output. Unlike classic pipeline maintenance strategies, pigging decreases downtime, mitigates energy intake, and extends the functional life of the pipeline, making it an practical and environmentally green practice. The procedure can be controlled or manually operated, depending on the specialized pipeline and required outcome.
Understanding Pigging Techniques:
Pipe Scraping steps offer a highly efficient approach for removing pipelines, especially within the mineral oil and energy gas field. Central to this is the pig – also called a brush – a strong, often cylindrical, instrument propelled by pressure differentials. Initially, a “launch station” forces the pig into the pipeline using a sequence of valves to build a pressure variation. This launch momentum sets the pig moving at a steady rate, influenced by pressure symmetry and pipeline traits. While traveling, the pig extracts deposits such as wax, scale, corrosion byproducts, and hydrate collections that hinder flow performance and may cause pipeline breakdowns. Subsequently, pipeline pressure reinstates behind the pig, enabling continued journey. At the end, a “receiving station” collects the pig, usually incorporating a pig housing that isolates the pig for inspection, and refurbishment if needed. The entire method is diligently observed to ensure pipeline durability and peak execution.
Pipeline Pigging Essentials, Sections, and Uses
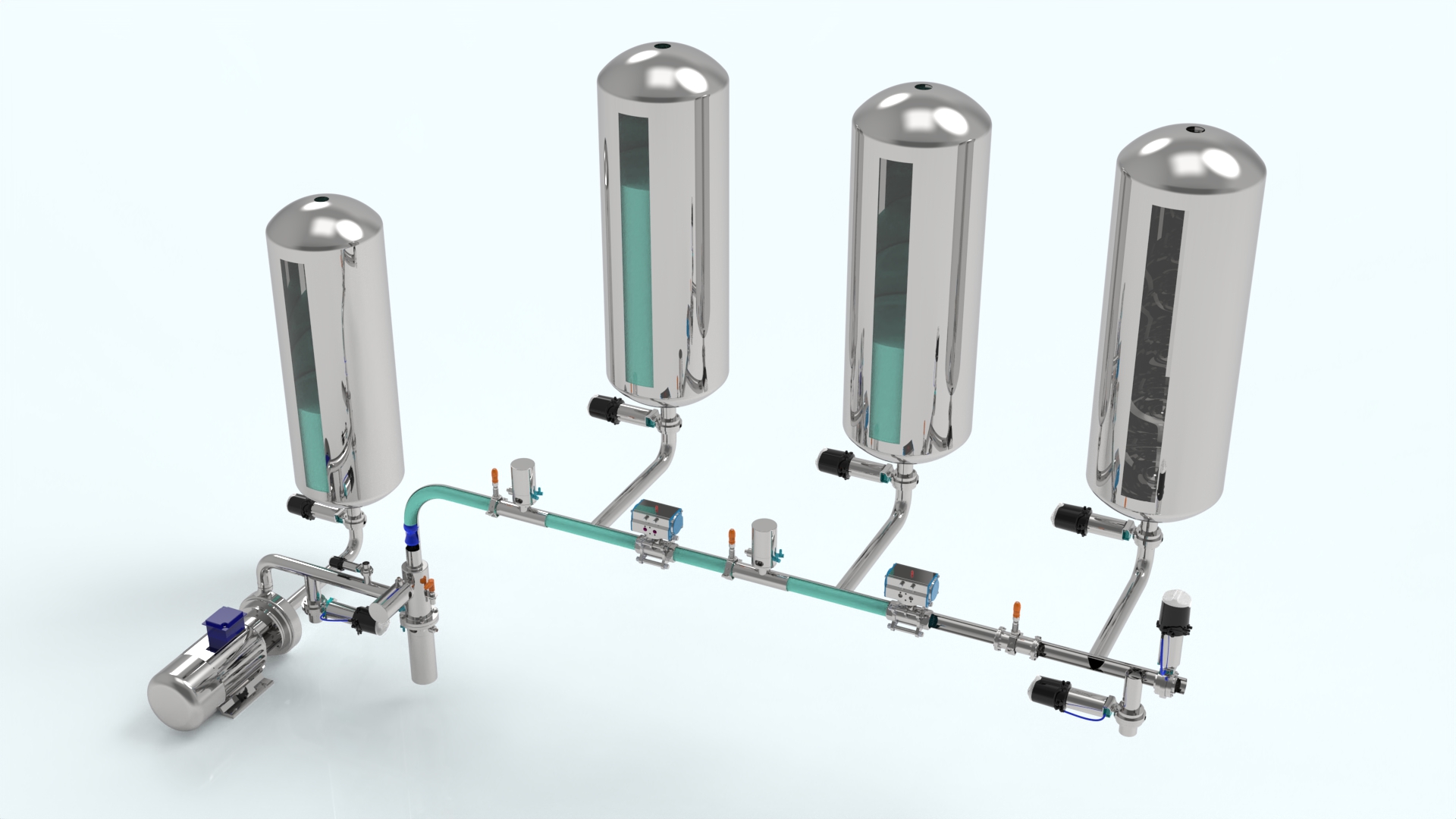
Pig Management accounts for an major process for preserving tubing integrity and operation across diverse sectors. The fundamental idea involves a specialized device named a "pig" traveling through the tubing to clean and inspect its internal surface. Such pigs, generally cylindrical in contour, are propelled by pressure imbalances, usually by injecting fluid before the pig and drawing it out afterward it. A typical pigging configuration features essential pieces, such as a launch station, receiver station, the pig itself – customizable for particular duties like cleaning, gauging, or inspecting – and a control unit. Applications reach wide spectra, from the industrial oil and gas environment removing deposits and ensuring stable flow, to the hydration sector for cleaning water mains, and chemicals industry for transporting and maintaining product lines. Efficient pigging operations limit operational expenditures, limit downtime, and importantly, enhance safer and more reliable system maintenance.
One Technique of Line Cleaning and Examination
The brushing practice, a fundamental aspect of maintaining passage reliability, is a surprisingly complex scientific accomplishment. It fundamentally involves inserting a unit called a “pig” into the pipeline and pushing it by compressed air. This implement removes sediment such as pitting found on internal walls, improving flow output and deterring costly blockages. Beyond basic cleaning, modern pigs are outfitted with high-tech gauges for detailed internal surveillance. These implements detect flaws, measure wall thickness, and spot diverse anomalies, delivering critical data for predictive upkeep and proactive repairs, thus minimizing risk and prolonging pipeline longevity. This process merges mechanical creativity with data interpretation to bolster sturdy infrastructure longevity.
Introduction to Pigging:
Industrial Pipeline Cleaning, a essential part of pipeline systems, comprises employing a instrument known as a “pig” to purge pipelines. This system holds extensive use across domains such as hydrocarbon, aqueous supply, and fabrication fields. The merits include enhanced flow operation, decreased product shrinkage, preserved pipeline condition, and reduced maintenance expenditures. Various styles of pigs exist, typically segregated as cleaning pigs that remove deposits, inspection pigs equipped with sensors to spot defects, and two-way pigs for flexible implementation. Proper pig choice requires evaluating duct material, diameter, fluid parameters, and anticipated hindrances. Thorough pig selection is vital to maximize results and minimize complications.
Examining Pigging System Capability
One careful evaluation of pigging mechanism activity illustrates a surprisingly intricate set of events. The rudimentary principle propels a ‘pig’ – a tailored device – through a tube via a positive displacement unit. This powering serves multiple intentions, including debris elimination, pipeline revival of integrity, and delivery refinement. The inclusive operation is carefully managed, with influencing factors including pig speed, launch and receiving compression, along with pig configuration. These elements play a vital role in locking the intended outcome. Additionally, innovative approaches integrate sophisticated assessment tools enabling real-time analysis and fine-tuning of pigging operations, substantially enhancing performance and abating downtime.
Fluid Pipeline Management Framework: Important Considerations and Preferred Standards
Effective channel pigging layout demands attentive evaluation of multiple significant aspects. Choosing the fitting pig style is paramount, with factors like line diameter, material fitness, and nature of contaminations to remove considered. A sturdy pigging setup must incorporate comprehensive stress drop monitoring to detect blockages or damage early. Additionally, insertion and acceptance depots must be optimally located to promote efficient pig progression and limit downtime. Routine monitoring and inspection of the pigging installation are essential to sustain optimum capability and prolong its duration. Finally, adherence to safety standards is mandatory, addressing potential hazards and securing the well-being of crew.
Repairing Pigging System Problems and Helpful Measures
Preserving peak pigging output often requires handling unexpected problems. Pressure drops surpassing acceptable standards are a common concern, typically due to leaks in the duct or a partially blocked pig. Regular examination of fittings and connections, alongside pig tracking methods, helps largely mitigate this risk. Another usual problem is pig damage, often caused by abrasive environments or improper pig choice for the designated task. Employing durable pigs with suitable wear resistance and carefully analyzing pipeline characteristics before deployment are crucial preventative steps. Moreover, pig cycling complications, such as incomplete sweeps or jammed pigs, may arise from inaccurate launcher or receiver pressure or internal pig malfunctions. Timely maintenance and pressure tests of these units, plus using pig bypasses where feasible, significantly assist in maintaining dependable pigging operations. Finally, ensuring chemical agent compatibility during pig cleaning is vital to avoid pipeline material deterioration.
Pipe Robustness Support Through Pigging: Preventing Corrosion and Fouling
Maintaining conduit soundness is crucial within the fuel and gas fields, where pigging, alternatively known as pipeline inspection, plays a vital role. These intelligent units, propelled through channels by pressure, meticulously remove substances and identify areas vulnerable to corrosion. Fouling, an accumulation of waxes, hydrates, and other residues, decreases transmission and provokes operational challenges. Simultaneously, often-invisible corrosion undermines pipe walls, creating safety hazards and risks. Regular pigging programs—utilizing cleaning pigs and inspection gadgets—proactively address these concerns, extending asset operational lifetime and minimizing costly, potentially devastating failures. Advanced pigging technologies now incorporate highly sophisticated sensors capable of assessing wall thickness and detecting even minute defects.
Progressive Pigging Devices: Data-driven Pigs and Metrics Recording
The transformation of duct integrity management introduced a new era of elaborate pigging methods, led by smart pigs and improved data collection capabilities. These sophisticated tools mark a major leap from traditional pigging, surpassing mere cleaning and debris removal. Modern intelligent pigs come with sensor arrays—including inline inspection tools for corrosion detection and geometric measurement—that continually gather data on pipeline condition. This information transmits real-time or post-run to surface systems, where it undergoes rigorous analysis to identify risk points and drive proactive maintenance strategies. Furthermore, enhanced data management offers finer, actionable insights, enabling targeted repair efforts and trimming unplanned downtime. Some advanced setups integrate machine learning and algorithms to forecast failures and optimize pigging schedules for optimal efficiency. Incorporating these technologies remains vital to safeguard safety, dependability, and lifespan of key infrastructure assets across varied sectors.
Ensuring Pipeline System Operation
Consistent pipeline cleaning mechanism inspection is absolutely crucial to maximize superior efficiency and lessen costly delays. This entails routine audits of pig equipment, including cup and wear ring quality, bushing efficiency, and launcher operation. Moreover, diligent and appropriate handling of the pig following each run is crucial. Neglect of these vital facets could provoke increased pressure reduction, damaged pipeline structures, and eventual operational breakdowns. Consequently, a proactive maintenance schedule—a detailed, planned regimen—is strongly recommended to guarantee long-lasting dependability and extend the endurance of pigging systems.
Thanks for your interest what is pigging